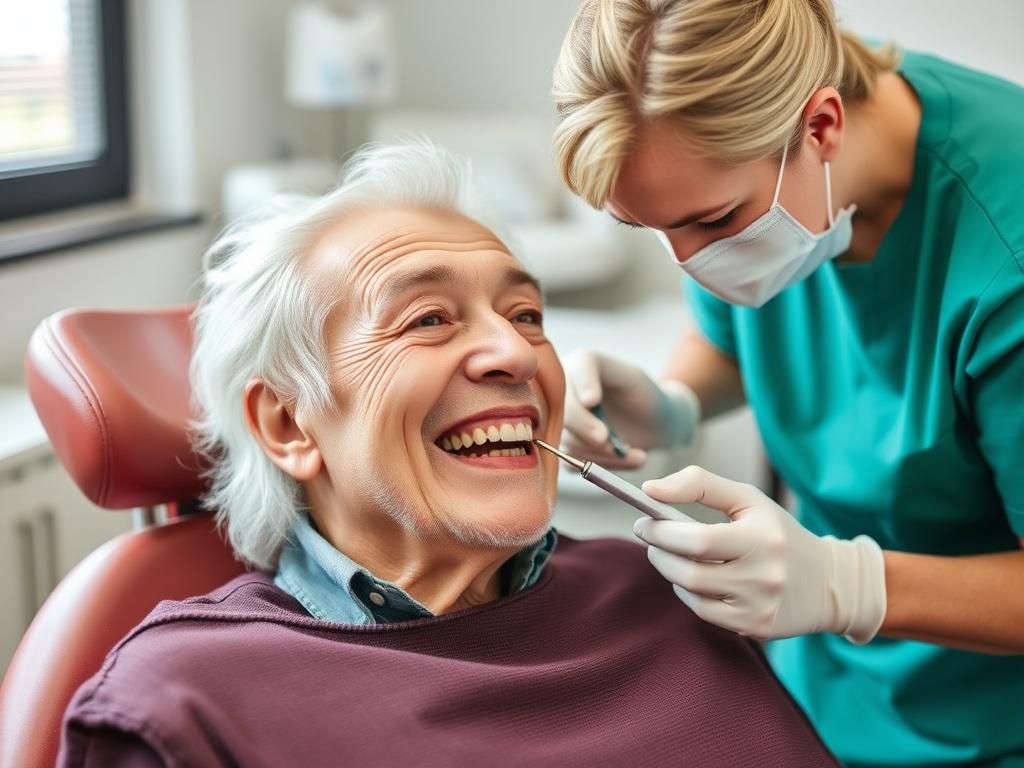
Dental care for seniors is a vital topic that often goes overlooked until problems arise. As we age, our oral health needs change, making it crucial to understand how to maintain a healthy smile throughout our golden years. Whether you’re a senior yourself, a caregiver, or simply interested in elder care, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know about dental care for seniors. From common dental issues and preventative measures to treatment options and tips for keeping your teeth and gums healthy, we’ve got you covered.
Содержание
- 1 Why Is Dental Care Important for Seniors?
- 2 Effective Dental Care for Seniors: Daily Practices
- 3 Regular Dental Visits: The Cornerstone of Senior Dental Care
- 4 Special Considerations in Senior Dental Care
- 5 Treatment Options Available for Seniors
- 6 Practical Tips for Seniors and Caregivers
- 7 Resources and Support for Senior Dental Care
- 8 Understanding the Link Between Oral Health and Overall Health
- 9 Innovations in Senior Dental Care
Why Is Dental Care Important for Seniors?
Aging brings many changes to the body, and the mouth is no exception. Dental care for seniors is essential because poor oral health can lead to pain, discomfort, and complications that affect overall well-being. Seniors are more susceptible to problems like tooth decay, gum disease, dry mouth, and tooth loss, which can interfere with eating, speaking, and social activities. Beyond these functional issues, poor dental health may also be linked to serious conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections.
Good dental care for seniors is about more than just preserving a beautiful smile. It’s about maintaining quality of life, independence, and even nutrition. When seniors have healthy teeth and gums, they can enjoy a varied diet without pain, communicate clearly, and feel confident in social settings. Regular dental checkups, proper hygiene, and awareness of common age-related issues are key elements in achieving these goals.
Common Dental Issues in Seniors
Understanding common dental issues in seniors helps in taking proactive steps to manage them effectively. Here are some of the most frequent dental challenges faced by older adults:
- Gum Disease: Also called periodontal disease, gum disease is a major cause of tooth loss in seniors. It starts with inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) and can progress to damage the bones and tissues supporting the teeth.
- Tooth Decay: Even though cavities are often associated with children, seniors can develop tooth decay, especially around older fillings or in roots exposed due to gum recession.
- Dry Mouth: Known medically as xerostomia, dry mouth is common in seniors because of medications and health conditions. Saliva is essential for protecting teeth and gums, so a lack of it raises the risk of decay and infection.
- Tooth Loss: Losing teeth can drastically affect eating ability and confidence. It’s often the end result of untreated decay or gum disease but can also be caused by trauma or other health factors.
- Oral Cancer: Seniors are at higher risk for oral cancers, making regular dental screenings crucial for early detection.
Effective Dental Care for Seniors: Daily Practices
Maintaining dental health for seniors isn’t complicated, but it does require consistency and some attention to changes in the mouth. Here are some essential habits to incorporate into daily routines:
Brushing and Flossing
Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste is fundamental to removing plaque and preventing decay. Using a soft-bristled toothbrush helps protect sensitive gums and reduces irritation. Electric toothbrushes can be a good option for seniors who have difficulty with manual dexterity.
Flossing is equally important to remove plaque and food particles from between teeth where brushing can’t reach. If traditional floss is difficult to handle, alternatives like floss picks or water flossers might be easier to use.
Hydration and Saliva Production
Dry mouth can be alleviated through hydration and certain diet adjustments. Drinking plenty of water, chewing sugar-free gum, and avoiding caffeine or alcohol that dehydrate the mouth can help stimulate saliva flow. There are also saliva substitutes available that dentists can recommend.
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports dental health. Seniors should aim to reduce sugary and acidic foods and beverages that contribute to tooth decay. Foods high in calcium, vitamin D, and phosphorous help strengthen teeth and bones, making dairy products, leafy greens, and nuts excellent choices for seniors.
Regular Dental Visits: The Cornerstone of Senior Dental Care
No matter how careful you are with home care, regular dental checkups are critical. Dentists can detect early signs of gum disease, cavities, oral cancer, and other issues that may not be obvious. For seniors, it’s recommended to visit the dentist at least twice a year, but some individuals may require more frequent appointments based on their health status.
What to Expect During Senior Dental Visits
Dental exams for seniors often involve:
- A thorough cleaning to remove plaque and tartar buildup.
- An evaluation of gum health and checking for signs of periodontal disease.
- Oral cancer screening, which usually includes visual inspection and sometimes palpation of the mouth and neck.
- Assessment of existing restorations such as dentures, crowns, or bridges.
- Discussion about medications and overall health that might impact oral care.
Seniors with cognitive impairments or physical disabilities may benefit from specialized dental care services, including home visits or treatment under sedation if necessary.
Special Considerations in Senior Dental Care
As people age, other health conditions and medications often complicate dental care. Paying attention to these factors ensures that dental treatments are safe and effective.
Medications and Their Impact
Many seniors take medications that cause side effects like dry mouth or increased bleeding, both of which affect oral health. Examples include antihypertensives, antidepressants, and anticoagulants. It’s important to inform the dentist about every medication being taken so they can adjust treatments accordingly.
Dental Care for Seniors with Dementia
Caring for seniors with dementia presents unique challenges. They may resist brushing or dental visits, and communication might be difficult. Caregivers can:
- Establish consistent routines to reduce confusion.
- Use gentle, calm approaches to oral hygiene.
- Seek dental professionals experienced in treating patients with cognitive impairments.
Use and Care of Dentures
Many seniors rely on dentures to replace missing teeth. Proper care of dentures is essential to prevent infections, bad breath, and damage to the mouth:
- Remove dentures overnight and soak them in a cleansing solution.
- Brush dentures daily to remove food and plaque.
- Have them checked regularly by a dentist for fit and comfort.
Treatment Options Available for Seniors

Dental care for seniors includes a wide range of treatment options, tailored to individual needs and health status. Here’s a quick look at some common treatments:
| Treatment | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Fillings | Restoration of decayed tooth areas using materials like composite resins or amalgam. | Stop decay and restore tooth function. |
| Scaling and Root Planing | Deep cleaning below the gumline to remove tartar and smooth root surfaces. | Treat gum disease and prevent tooth loss. |
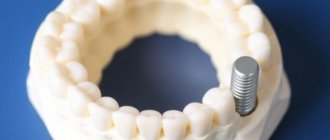
| Dental Implants | Surgical placement of an artificial tooth root to support crowns or dentures. | Replace missing teeth with durable, natural-looking alternatives. |
| Dentures | Removable artificial teeth replacing some or all teeth in the upper or lower jaw. | Restore ability to chew and improve appearance. |
| Root Canals | Treatment of infected tooth pulp to save a decayed or damaged tooth. | Relieve pain and avoid extraction. |
It’s essential to discuss all options with your dentist to choose the best plan that fits your health conditions, lifestyle, and budget.
Practical Tips for Seniors and Caregivers
Good dental care for seniors often involves teamwork between the individual, family members, and healthcare professionals. Here are some practical tips to make daily oral care easier and more effective:
- Set reminders: Use alarms or notes to remember brushing, flossing, and dental appointments.
- Choose the right tools: Select toothbrushes with larger handles or electric brushes for easier grip.
- Maintain regular routines: Consistent times for brushing and cleaning dentures help create habits.
- Be patient: Dental care can be uncomfortable when gums are sensitive or dry, so approach with care and gentleness.
- Monitor medications: Review any changes with both doctors and dentists to catch possible side effects affecting oral health.
- Encourage hydration and healthy eating: This supports saliva flow and strengthens teeth naturally.
Resources and Support for Senior Dental Care

Navigating dental care for seniors can sometimes be challenging due to financial, mobility, or health issues. Thankfully, there are resources to help:
- Medicare and Medicaid: While original Medicare doesn’t cover most dental care, some Medicare Advantage plans include dental benefits. Medicaid coverage varies by state.
- Community Clinics: Many areas have dental clinics offering reduced-cost services for seniors.
- Home Dental Care Services: For seniors with mobility issues, some providers offer in-home dental care or mobile dental units.
- Educational Materials: Organizations like the American Dental Association provide free guides on senior oral health.
If you’re a caregiver, don’t hesitate to seek support groups and training to better assist your loved ones with their dental care needs.
Understanding the Link Between Oral Health and Overall Health

Research has consistently shown that oral health is closely connected to overall health. For seniors, this link is even more important to consider. Gum disease, for example, has been associated with an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, diabetes complications, and respiratory infections. Managing dental care for seniors is therefore not just about protecting teeth, but also about improving holistic health outcomes.
Studies indicate that inflammation from gum disease can impact systemic inflammation in the body, worsening chronic illnesses. Additionally, poor oral health can affect nutrition by making eating painful or difficult, which can lead to weakened immunity and slower recovery from illness.
Innovations in Senior Dental Care
With advances in dental technology, many traditional barriers faced by seniors in maintaining oral health are being addressed:
- Digital Imaging: Allows for more accurate diagnosis and less invasive examinations.
- Improved Denture Materials: More comfortable, natural-looking, and easier to maintain dentures increase compliance.
- Teledentistry: Remote consultations can help seniors get preliminary advice without the need for travel.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: New approaches cause less pain and quicker healing times.
Staying informed about these innovations can help seniors access better care and make well-informed decisions.
Conclusion
Dental care for seniors is a vital aspect of healthy aging that deserves attention and priority. As we have explored, seniors face unique oral health challenges, but with proper daily care, regular dental visits, and awareness of special considerations, it is very possible to maintain a strong, comfortable, and beautiful smile. By understanding common conditions, adapting routines, and utilizing available treatment options and resources, seniors and their caregivers can improve both oral and overall health. Remember, a healthy smile in later life is not just about teeth—it’s about preserving dignity, enjoyment, and quality of life every day. So, whether you are a senior or someone who supports them, investing time and effort into dental care will pay immense dividends for years to come.